A binding minimum wage causes the quantity of labor demanded to exceed the quantity of labor supplied.
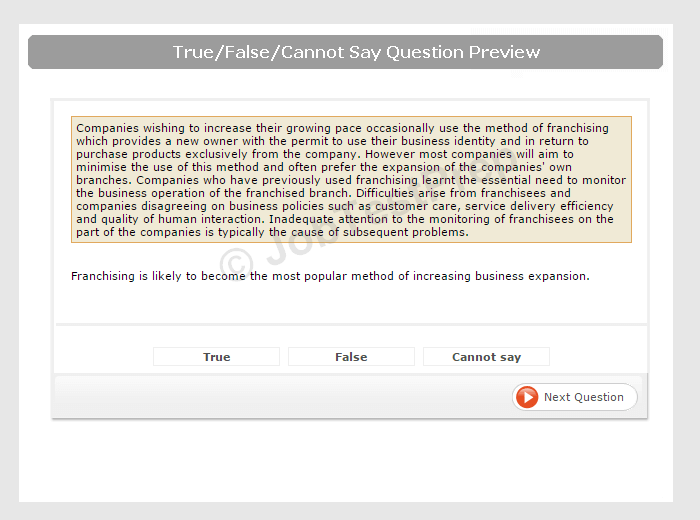
The minimum wage is an example of a price floor a true b false.
50 an excess supply occurs at prices below the equilibrium price.
See how much you know about price controls by answering true or false to these questions.
Imposed by government below equilibrium price b.
When the minimum wage is set above the equilibrium market price for.
A price floor sets the lowest legal price and that is precisely what a minimum wage does.
A non binding price floor causes a change in the market price.
In modern western countries labor is the primary recipient of price floors 1 in particular the government imposes a minimum wage making it illegal for an employer to pay a worker less than a certain amount per hour.
An example of a price floor is minimum wage laws where the government sets out the minimum hourly rate that can be paid for labour.
Tariffs increase equilibrium price and quantity.
Discrimination is an example of a rationing mechanism that may naturally develop in response to a binding price floor.
In a labor market a minimum wage is an example of a price floor.
Like price ceilings price floors disrupt market cooperation and have consequences quite different from those advertised by their advocates.
The minimum wage is an example of a price floor.
When a binding price floor is imposed on a market for a good some people who want to sell the good cannot do so.
It sets the lowest legal wage rate.
A tax on buyers increases the size of a market.
A price floor causes excess demand resulting in the need to ration by some means other than price.
A true b false 49 a minimum wage set below the market equilibrium wage will result in higher unemployment.
In this case the wage is the price of labour and employees are the suppliers of labor and the company is the consumer of employees labour.
A binding price ceiling is best defined as a price.
The minimum wage is an example of a price ceiling.
The minimum wage is an example of a price floor.
48 minimum wage is an example of a price floor.
Before considering an example of price floors minimum wages let s examine the problem in general terms.
Price floor causing excess supply in the market.
True studies by economists have found that a 10 increase in the minimum wage decreases teenage employment by 10.
In those states that impose such a minimum wage it is more likely that the minimum wage acts as a binding.
A surplus may result in an alternative rationing mechanism being developed.